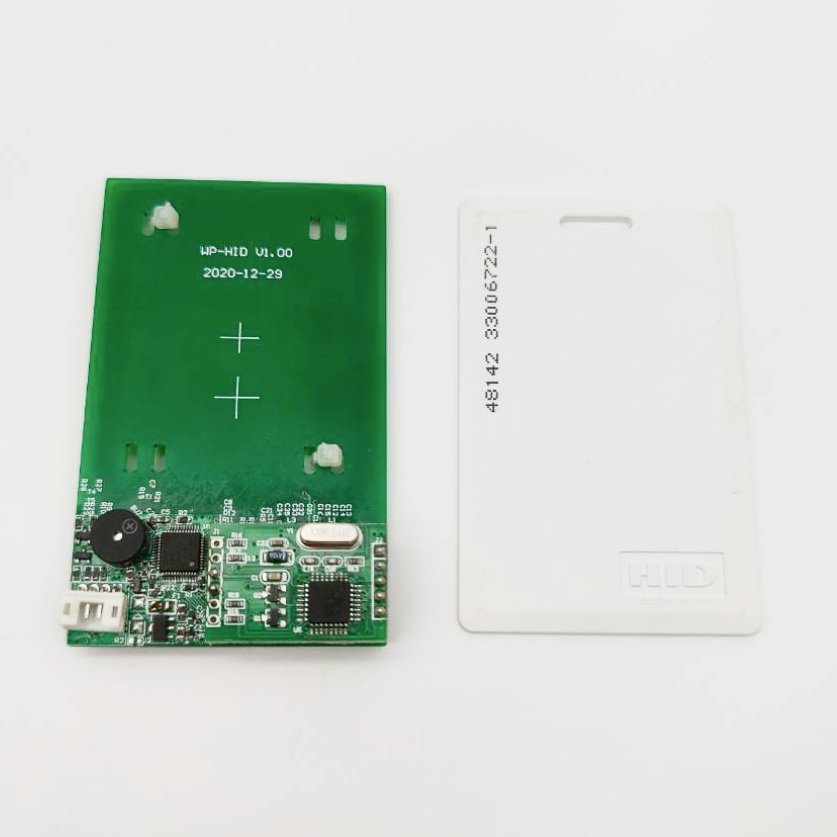
The 26-bit Wiegand format is one of the most widely used standards for access control systems, particularly in legacy installations.
It’s an open format, meaning that any organization can implement and use it, and multiple manufacturers produce cards compatible with this system.
What Is the Standard 26-Bit Wiegand Format?
At its core, the 26-bit Wiegand format is a method of encoding binary data to identify individuals via access cards, key fobs, or other devices.
The term “bit” refers to the smallest data unit, either a 0 or a 1, which makes up the digital code stored on these cards. The format follows a structured design where the data is split into three main components:
- Bits: The first and last bits in the 26-bit sequence are parity bits. These are used for error checking to ensure the data is transmitted correctly, but they do not contribute to the unique identification number on the card.
- Facility Code: The second through ninth bits (8 bits in total) represent the facility code or site code. This code identifies the specific location or organization that issued the card. The facility code can range from 0 to 255, allowing for 256 unique facility codes.
- Card Number: Bits ten through twenty-five (16 bits) store the ID number assigned to the individual cardholder. This number can range from 0 to 65,535, meaning there can be over 65,000 unique cardholders per facility.
When combined, the 26-bit format provides 16,711,425 unique card combinations (256 facility codes multiplied by 65,536 card numbers), making it a popular choice for standard access control systems.
How Does the 26 Bit Wiegand Format Work?
The Wiegand format is named after John R. Wiegand, who discovered the principle behind it in the 1970s. He found that certain metal wires change polarity when exposed to a magnetic field, which could be used to transmit binary data. This discovery laid the foundation for modern access control systems.

Access cards using the 26-bit Wiegand format have a simple structure consisting of three wires inside: data0, data1, and ground. These wires transmit binary signals (0s and 1s) to the reader. When a card is scanned, the reader detects the signal changes from the data0 and data1 wires, converting the signals into the corresponding binary sequence.
- When the data0 wire sends a signal, it is read as a 0.
- When the data1 wire sends a signal, it is interpreted as a 1.
Once the reader receives this data, it decodes the information, checks the parity bits for accuracy, and then compares the facility code and card number to the stored database. Access is granted if the facility code and card number match the authorized entries in the system. If not, access is denied.
Why Is the Wiegand 26-Bit Format Still in Use in Access Control?
Despite being a relatively older technology, the 26-bit Wiegand format remains in use for several reasons:
- Simplicity: It’s easy to implement and integrate with many existing access control systems. Most access control systems automatically support the 26-bit format, making it convenient for organizations to adopt without requiring complex configurations.
- Availability: The open nature of the 26-bit Wiegand format means that it’s widely available. Many manufacturers produce prox cards in this format, which has led to its continued use in older buildings and facilities that prioritize cost-efficiency over cutting-edge security.
However, there are security concerns. Since the 26-bit format is not encrypted and duplicates can be created, it’s not suitable for high-security environments.
As technology has evolved, more secure formats like OSDP (Open Supervised Device Protocol) have been developed to offer encryption and enhanced security features.
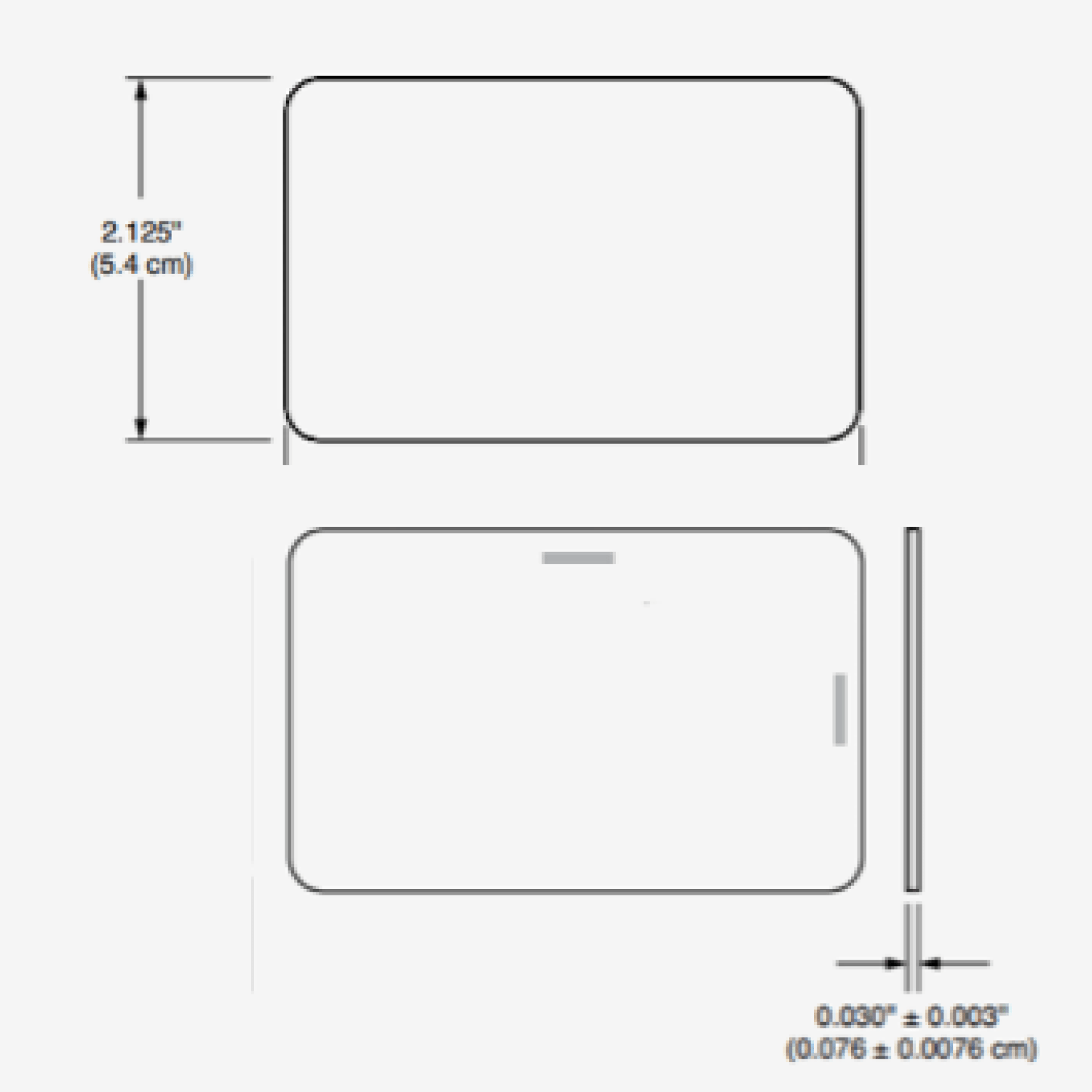
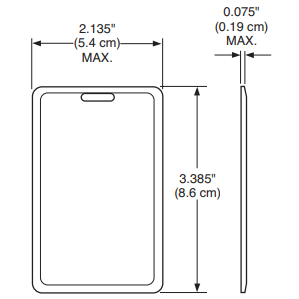
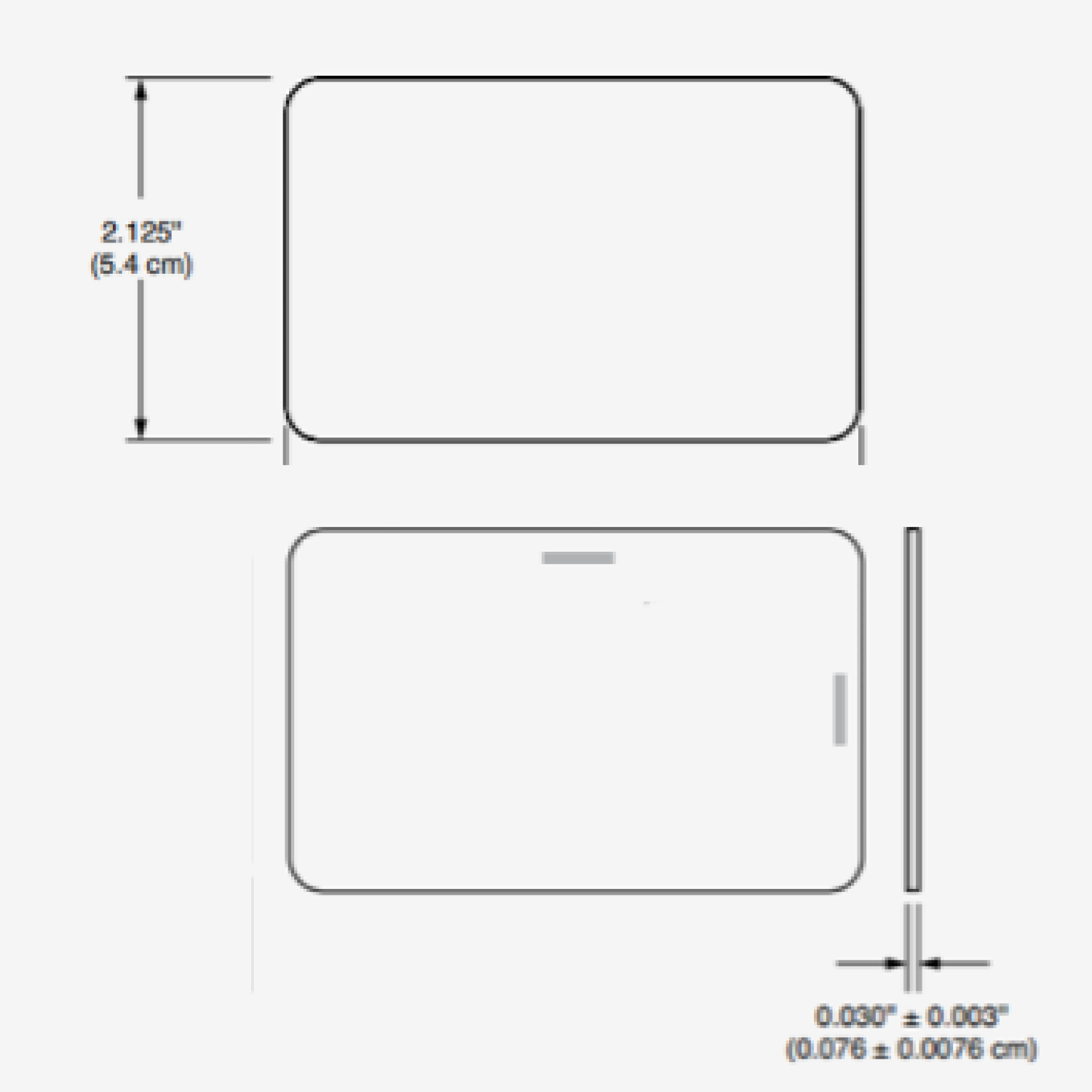
FREE 26-bit Wiegand H10301 Format Prox Card
Are You Tired of Paying A Premium for Name-Brand Proximity Cards?
Our H10301 Format 26 Bit Wiegand Proximity cardsmoffer the same reliable performance as the premium name brand cards.
We're offering a chance to try them FOR FREE.
How to Identify if Your System Uses the 26-Bit Wiegand Format
To determine whether your access control system or card uses the 26-bit Wiegand format:
Check the Documentation
The easiest way is to check the system or card documentation, which often includes details on the card format, facility code, and card range.
Look for the H10301 Identifier
The H10301 format is a common name for the 26-bit Wiegand format. If this is listed on your card packaging or system, it confirms that the format is in use.
Consult Your Access Control Provider
If you’re unsure about the format, contact your access control provider. They can usually confirm the card format based on the equipment and system configuration.
Use a Card Reader
You can also scan the card with a card reader to retrieve the facility code and card number. Many readers will display the card’s bit length, and if the card contains 26 bits, it’s likely using the Wiegand H10301 format.