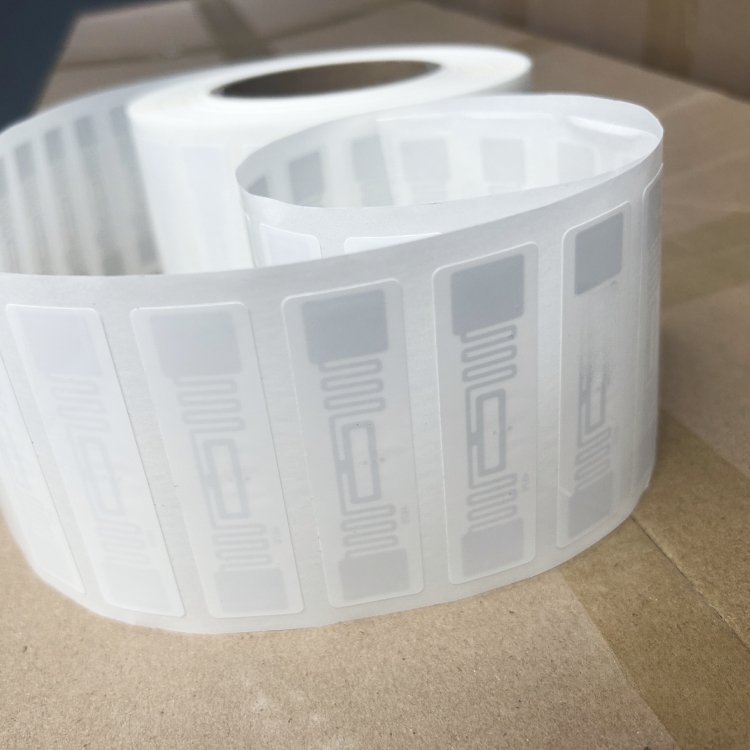
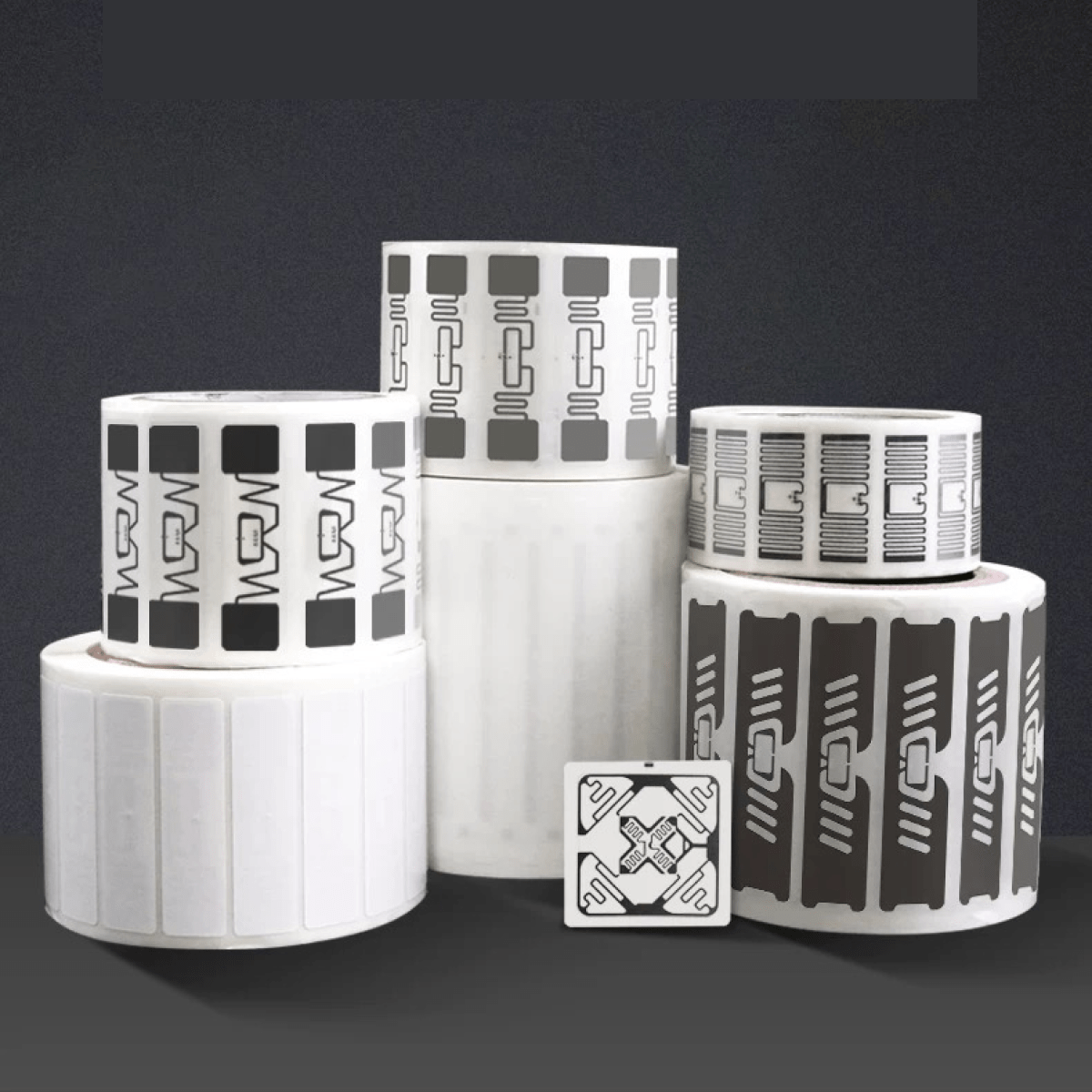
In today’s world, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized the way we can track and manage assets, inventory, and information. This innovation has been a game-changer for the industry, enabling more efficient and accurate tracking of inventory, assets, and data across various sectors.
Within this domain, there are two types of RFID systems, Active and Passive RFID play pivotal roles, each with unique characteristics and applications. This article delves into the differences between these two types of RFID systems, their advantages, and considerations for their implementation.
Key Takeaways
Active RFID
Pros
Active RFID tags are equipped with their own power source, typically a battery. This allows for greater read range, improved data storage, and transmission capabilities. They can actively transmit data, making them ideal for real-time tracking and long-range communication.
Applications
These tags are often used in large-scale asset tracking, such as in logistics and transportation, where real-time location data is crucial. They are also employed in high-value asset tracking in hospitals and large retail environments.
Passive RFID
Pros
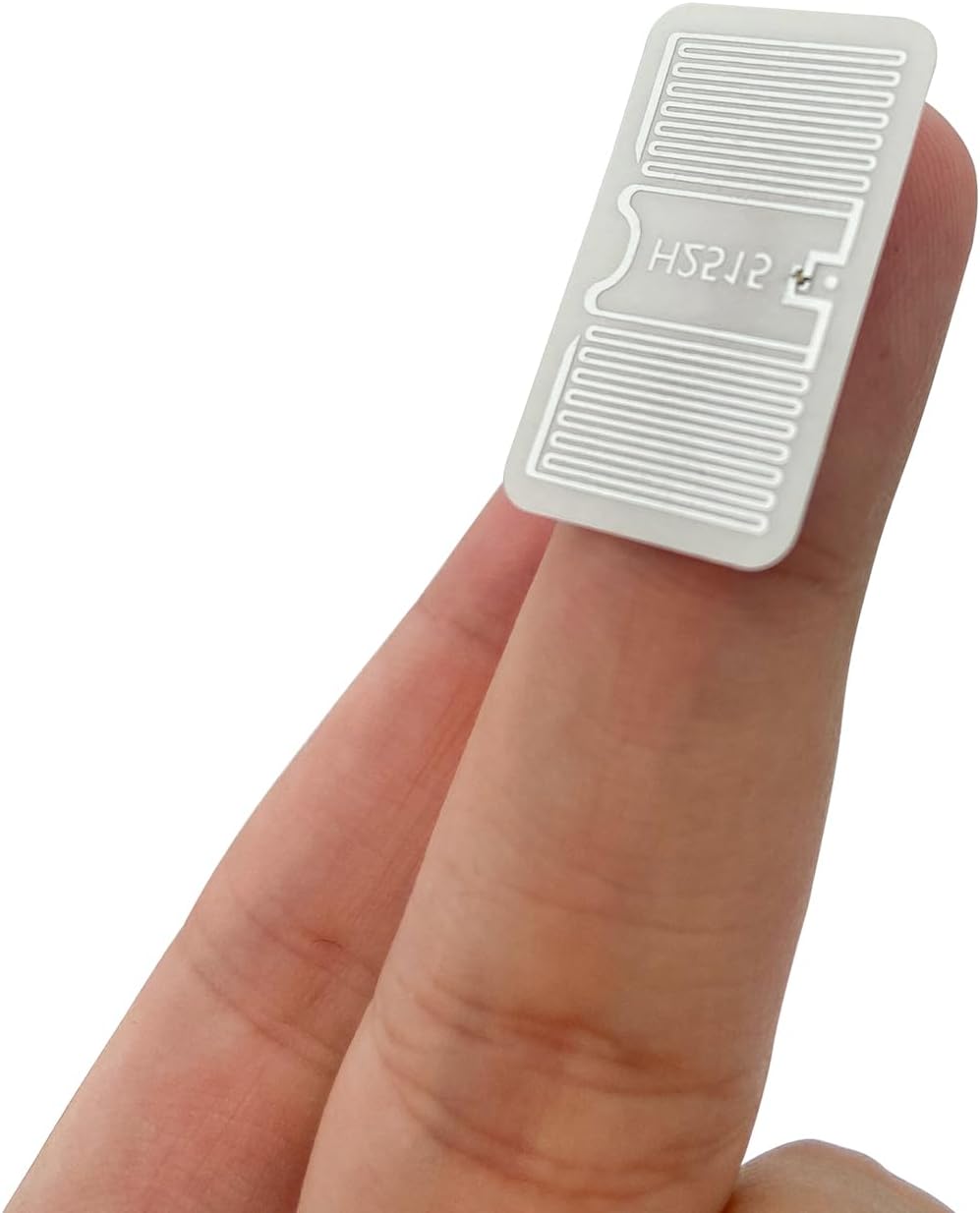
Passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source. They are powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from RFID readers. This makes them smaller, lighter, and significantly cheaper than active tags. They are also maintenance-free, with a longer lifespan.
Advantages
Passive RFID technology is widely used in supply chain management, retail inventory tracking, and access control systems. They are also popular in applications where bulk tagging of items is required, such as in libraries or file tracking.
Key Differences: Active RFID Vs Passive RFID
Range of operation
When we talk about the range of operation of RFIDs, Active RFID clearly has more range than Passive RFID. Active RFID tags can be read from distances of 100 feet or more, while passive tags typically have a read range of up to 20 feet.
Battery requirements
Active tags require a power source, usually a battery, whereas passive tags are powered by the reader’s signal. Active tags don’t have a long lifespan and require a battery swap every 3-4 years。
Cost
Passive RFID tags are significantly cheaper, sometimes costing a few cents approx 0.09$ per tag, compared to active tags which can be several dollars each.
Data storage and transmission capabilities
Active RFID tags can store more data and transmit it over greater distances, offering enhanced functionality.
Reliability and durability
Passive tags are more reliable in harsh conditions and have a longer lifespan as they don’t contain batteries. Also, passive tags are easy and convenient to print directly from the RFID Printer.
Types of Passive RFID Tags & Labels
Inlays
Inlays are the most basic form of RFID tags and are generally categorized based on their construction and application methods, commonly known as Passive RFID tags.
Dry Inlays
Dry inlays consist of an RFID chip and antenna and are typically encased in a thin layer of material without any adhesive. These are the simplest and most cost-effective type of RFID inlays, ideal for applications where the tag is not exposed to significant wear and tear. They are commonly used in applications where they can be enclosed or protected, such as within product packaging or labels.
Wet Inlays
Wet inlays are similar to dry inlays but come with an adhesive backing, making them ready for application to various surfaces. The adhesive and the thin lamination make wet inlays slightly more durable than dry inlays. They are widely used in retail for item-level tagging, supply chain management, and asset tracking where quick and easy application to products is necessary.
Paper Face Tags
Paper face tags are a type of wet inlay that has an additional paper layer, allowing for printing. This feature makes them highly versatile, as they can be printed with barcodes, logos, or other information. They are commonly used in retail environments for price labeling and product information.
Hard Tags
Hard tags are designed for more demanding environments and applications, offering enhanced durability and functionality.
Hard tags come in various sizes and can be made from different materials, catering to specific needs based on the application. The choice of size and material often depends on factors like the required read range, the environment in which the tag will be used, and the type of surface to which it will be attached.
High-Temperature Tags
These tags are built to withstand extreme temperatures, making them suitable for industrial environments like manufacturing or processing plants where heat resistance is crucial.
Rugged Tags
Rugged tags are designed to endure harsh conditions and rough handling. They are typically encased in a durable material like plastic or metal, making them ideal for outdoor use, heavy machinery, or in situations where they might be subject to physical stress.
Embeddable RFID Tags
These tags are designed to be embedded into products or assets. Embeddable RFID tags are particularly useful in manufacturing, where they can be integrated into product components for tracking throughout the production process and lifecycle management.
Type of Active RFID Tags
Transponders
Transponders are active RFID tags that are designed to respond when they receive a signal from an RFID reader. Their active nature allows for a longer read range compared to passive tags. These tags are typically used in situations where assets need to be tracked over long distances or in large-scale environments, such as in logistics for tracking shipping containers or in vehicle tracking systems. The ability of transponders to provide real-time location data makes them invaluable in dynamic tracking scenarios.
Beacons
Beacons represent another type of active RFID tag, known for their ability to transmit signals at set intervals autonomously. This feature allows for continuous monitoring of assets without the need for a triggering signal from a reader. Beacons are particularly useful in scenarios where constant tracking is required, such as monitoring the movement of goods within a large warehouse or tracking high-value equipment in healthcare facilities. Their autonomous signaling capability ensures that assets are consistently visible and trackable within the system.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Passive and Active RFID
When selecting between passive and active RFID technologies for your business, several critical factors must be considered to ensure that the chosen solution aligns effectively with your operational needs. Understanding these factors is essential for making an informed decision that not only meets current requirements but also accommodates future growth and changes.
Business Needs
First and foremost, assess the specific needs of your business. If real-time tracking and long-range communication are essential, such as in logistics or asset management, active RFID might be the better choice. Conversely, if your focus is on cost-effective inventory management or asset tracking over shorter distances, passive RFID could be more suitable. The decision should align with your operational priorities and the desired outcomes of the RFID implementation.
Budget Constraints
Budget is a significant consideration. Active RFID tags are generally more expensive than passive tags due to their advanced features and built-in power sources. For businesses with limited budgets or those requiring a large number of tags, passive RFID may be the more financially viable option.
Technical Requirements
Evaluate the technical requirements of your RFID system. Consider factors like read range, memory capacity, and the environmental conditions in which the tags will be used. Active RFID offers a greater read range and larger memory capacity, which is beneficial in complex tracking systems. Passive RFID, however, is more suitable for simpler, proximity-based applications.
Scalability
Finally, consider the scalability of the system. If your business anticipates significant growth or changes in tracking needs, choose a technology that can adapt and scale accordingly. Active RFID systems are typically more flexible and scalable due to their higher range and data transmission capabilities, making them suitable for evolving business environments.