Quali sono le differenze? Card RFID vs HID vs Mifare vs Card di prossimità
Risposte rapide
Quali sono i diversi tipi di RFID?
Cos'è l'HID rispetto all'RFID?
Le card di prossimità HID sono RFID?
Qual è la differenza tra prossimità e RFID?
Qual è la differenza tra NFC e HID?
Guida rapida: Quali sono le differenze?
RFID vs. Prossimità
L'RFID
Prossimità
LF: 120–135 kHz (ad es. HID Prox, EM)
HF: 13,56 MHz (ad es. MIFARE, iCLASS)
UHF: 860–960 MHz (RAIN RFID)
LF: 125 kHz (più comune)
LF: fino a 6 piedi (1,8 metri)
HF: fino a 3 piedi (1 metro)
UHF: 25–33 piedi (7,5–10 metri)(con tag speciali: fino a oltre 300 piedi/91+ metri)
In genere 2–6 pollici (5–15 cm), raramente fino a 2 piedi (60 cm)
Lettura e scrittura (i dati possono essere aggiornati o modificati)
Sola lettura (numero ID fisso, non modificabile)
Controllo accessi, pagamenti, inventario, tracciamento dei beni, rilevazione presenze, passaporti elettronici, biblioteche
Controllo accessi, pagamenti, inventario, tracciamento dei beni, rilevazione presenze, passaporti elettronici, biblioteche
Avanzato: crittografia (AES, DES), autenticazione reciproca, archiviazione sicura dei dati
Principalmente per il controllo degli accessi monouso
HF/UHF: velocità di trasferimento dati 50–424 kbps (dipende dal protocollo e dal tipo di scheda)
Molto veloce (solo controllo ID, <100 ms tipico)
MIFARE Classic, MIFARE DESFire, HID iCLASS, LEGIC, UHF EPC Gen2
HID Prox, EM Prox, AWID, Indala
Schede HF/UHF: fino a 4 KB (kilobyte) o più (ad es., MIFARE DESFire EV2: fino a 8 KB)
24–40 bit (3–5 byte), solitamente solo un numero ID
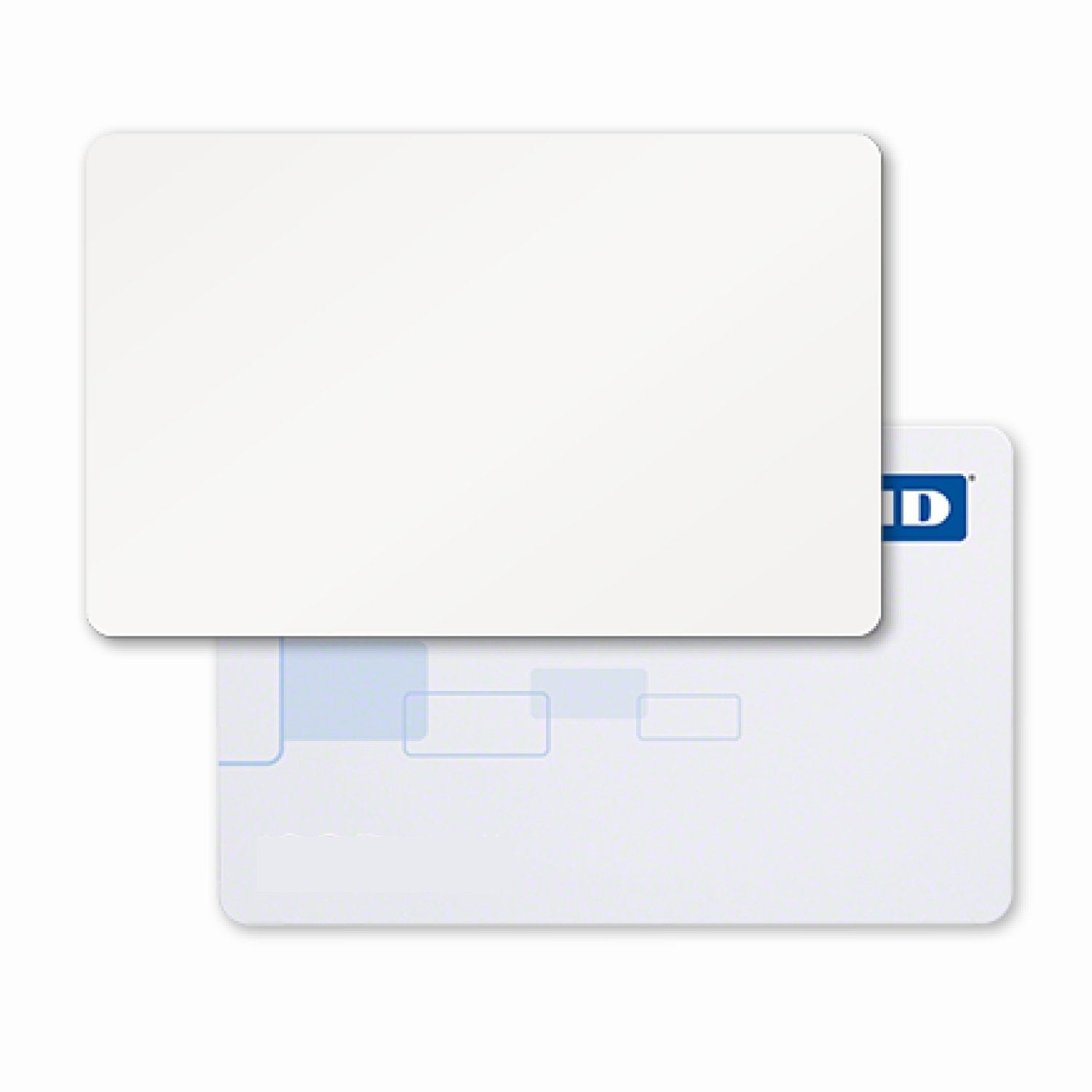
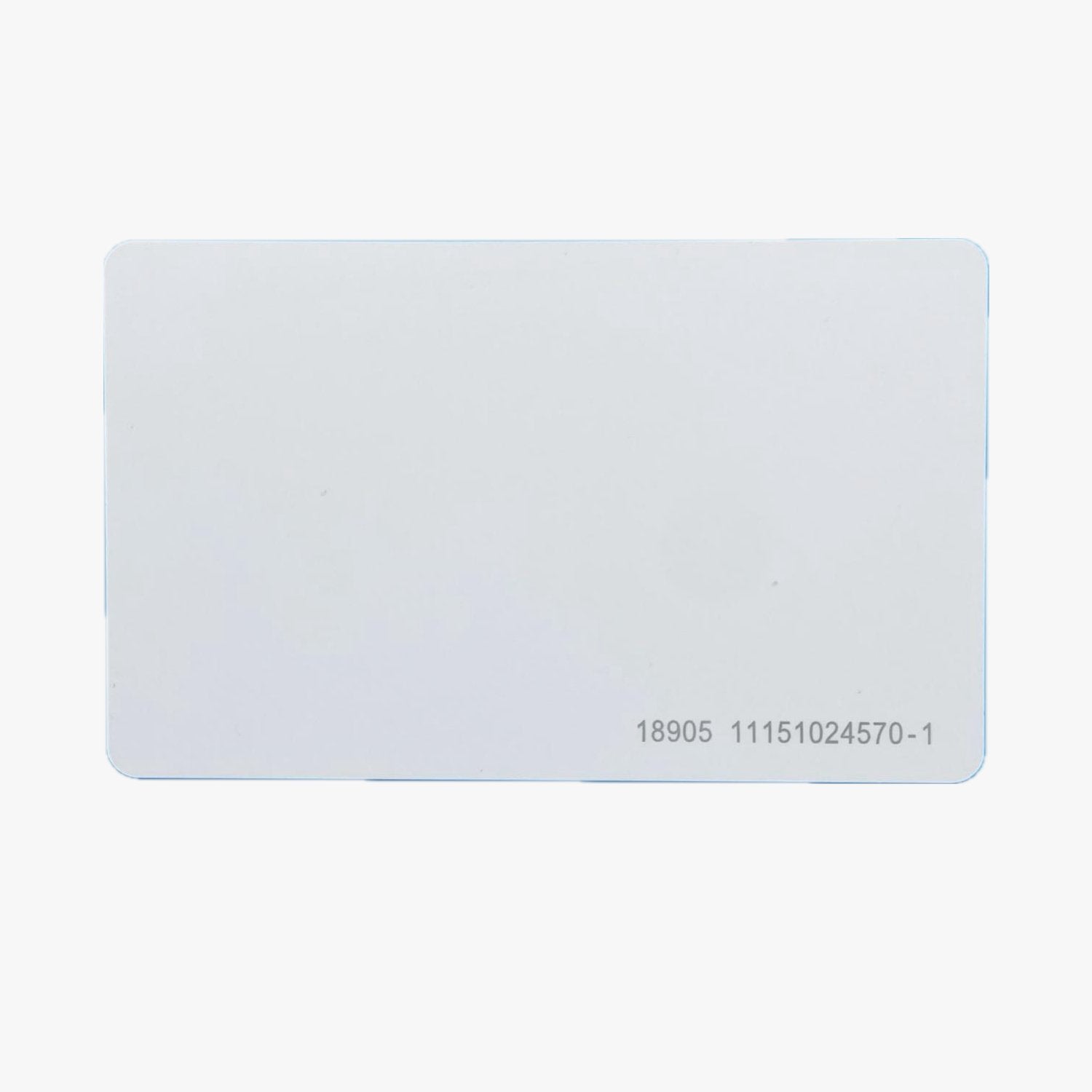



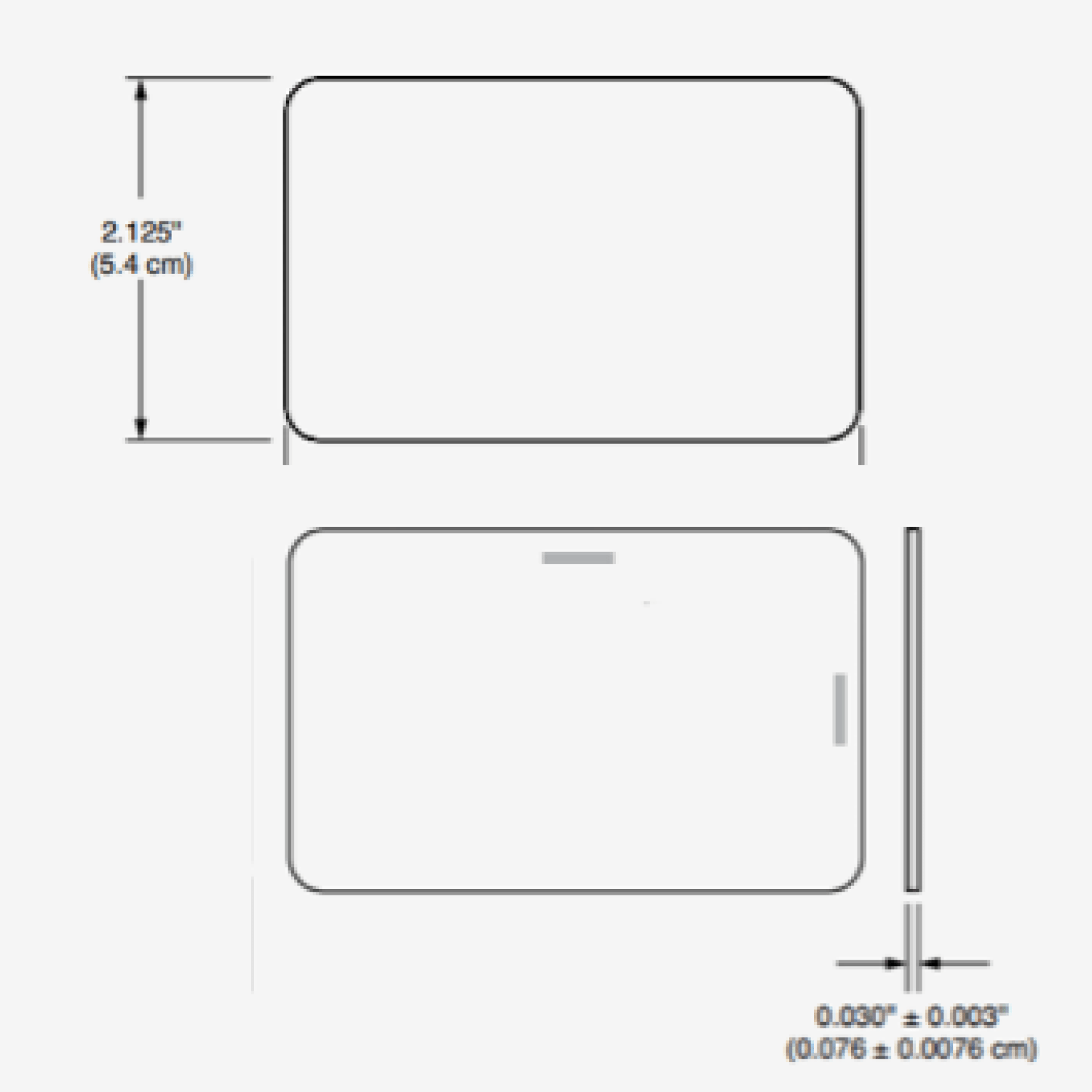

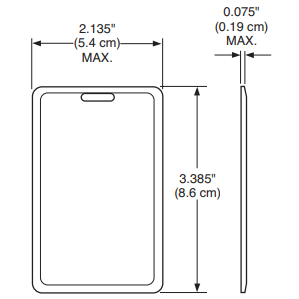



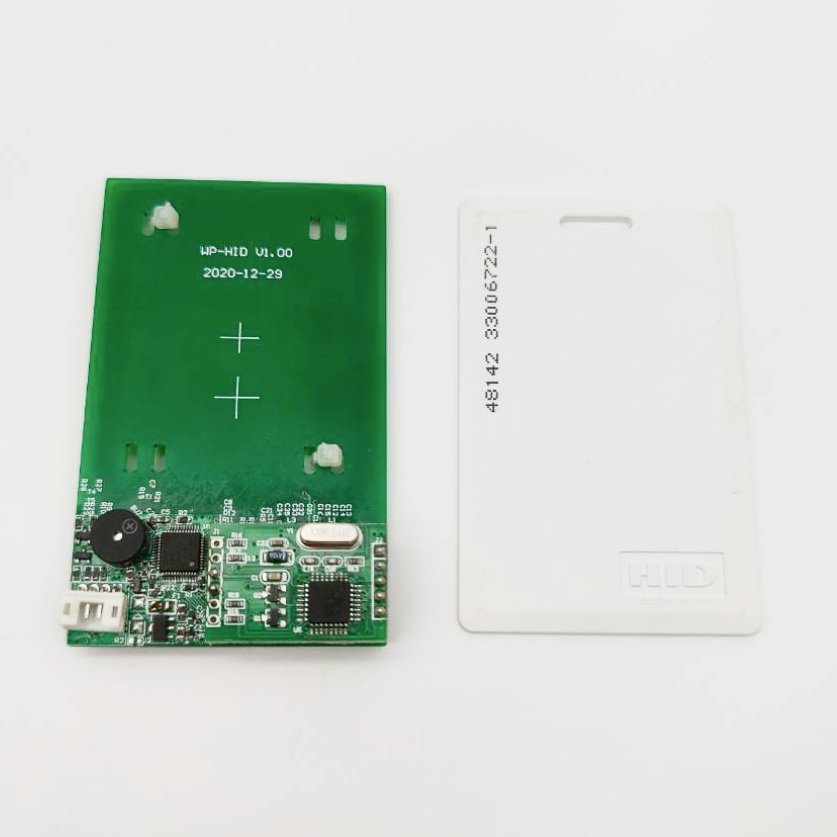
Carte di prossimità H10301 formato 26-bit che funzionano esattamente come le HID H10301 ProxCard II. Stampabili su misura.
Guida comparativa: Quale tipo di carta scegliere?
Mifare vs. HID vs. Prossimità
Carte MIFARE
Tessere di prossimità
Schede HID (Prox, iCLASS, Seos)
RFID ad alta frequenza da 13,56 MHz, compatibile con NFC
RFID a bassa frequenza da 125 kHz
125 kHz (Prox), 13,56 MHz (iCLASS/Seos)
Avanzate: autenticazione reciproca, crittografia (DES/AES)
Base: solo numero ID, nessuna crittografia, facilmente clonabile
Prox: Base (non crittografato); iCLASS/Seos: Avanzato (AES, autenticazione reciproca)
1–4 KB (MIFARE Classic), fino a 8 KB (DESFire EV2)
24–40 bit (3–5 byte), numero ID fisso
Prox: 24–40 bit; iCLASS: fino a 32 KB, multi-applicazione
Lettura/scrittura, supporta più applicazioni
Di sola lettura, non può essere aggiornato
Prox: Sola lettura; iCLASS/Seos: Lettura/scrittura
2–4 pollici (5–10 cm)
2–6 pollici (5–15 cm), fino a 10 cm (3,9 pollici)
Prox: 2–6 pollici; iCLASS/Seos: fino a 4 pollici (10 cm)
Transito, accesso sicuro, vendita senza contanti, ID, fedeltà
Accesso base a porte/edifici, orari e presenze
Prox: Accesso alla porta; iCLASS/Seos: accesso sicuro, biometria, pagamento
Sì (DES, 3DES, AES, autenticazione reciproca)
No
Prox: No; iCLASS/Seos: Sì (AES, autenticazione reciproca)
Richiede un lettore da 13,56 MHz
Richiede un lettore da 125 kHz
Prox: lettore da 125 kHz; iCLASS/Seos: lettore da 13,56 MHz
Perché spendere molto per card di marchi premium?
Quando risparmi il 60% sul tuo budget
Spedizione GRATUITA inclusa. Tutto a carico nostro!














